Low birth weight and premature babies are at risk of a number of problems – it is important to try and anticipate these, and to recognise and treat if necessary.
Small babies should be fed every 3 hours (by breast or EBM by cup/NGT).
The daily feed volume should be calculated as below, and divided by 8 to give the 3-hourly feed volume. Use the birth weight for calculations untill the actual weight is above the birth weight!
| Day | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 onwards |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount/day | 60 ml/kg | 90 ml/kg | 120 ml/kg | 150 ml/kg | 150-200 ml/kg |
Example:
A baby with birth weight 1.6kg baby, now on day 3 of life with 1,5 kg, requires 120 ml x 1.6 kg = 192 ml/day ÷ 8 = 24 ml/feed
If the baby shows any signs of hypoglycaemia (lethargy, floppiness, convulsions, apnoea, abnormal neurological behaviour) please check the blood glucose level.
If it is not possible to check the blood glucose, go ahead and treat.
Emergency treatment of hypoglycaemia
Recheck after 30 minutes to ensure the blood glucose level has improved. |
Prevent hypothermia by keeping in hot cot/under heater and ensuring baby is well wrapped and wearing a hat.
If still hypothermic, try KMC even if they are on cpap/oxygen.
When the baby is stable, it should be nursed in 'Kangaroo' position.
If a baby is cold don't warm up faster than 1 C per hour.
Please ensure baby is well hydrated and DO NOT USE WARMED IV FLUID BAGS TO WARM THE BABY.
Premature delivery may be due to maternal infection. Have a very low threshold for starting antibiotics in premature babies. Remember that signs of sepsis in a newborn can be very non-specific Neonatal sepsis
(ALL BABIES WEIGHING <1500g TO BE STARTED ON ANTIBIOTIC)
Very premature babies lack surfactant and therefore may have marked respiratory distress.
Put the baby on O2, cover with antibiotics and ensure they are kept warm.
IF IN SEVERE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS AND >1000g CONSIDER CPAP.
See CPAP
Very premature babies have immature respiratory centres in the brain and sometimes "forget" to breath.
We use aminophylline as a respiratory stimulant for babies <34/40 gestation: 6mg/kg STAT, then 2.5mg/kg BD.
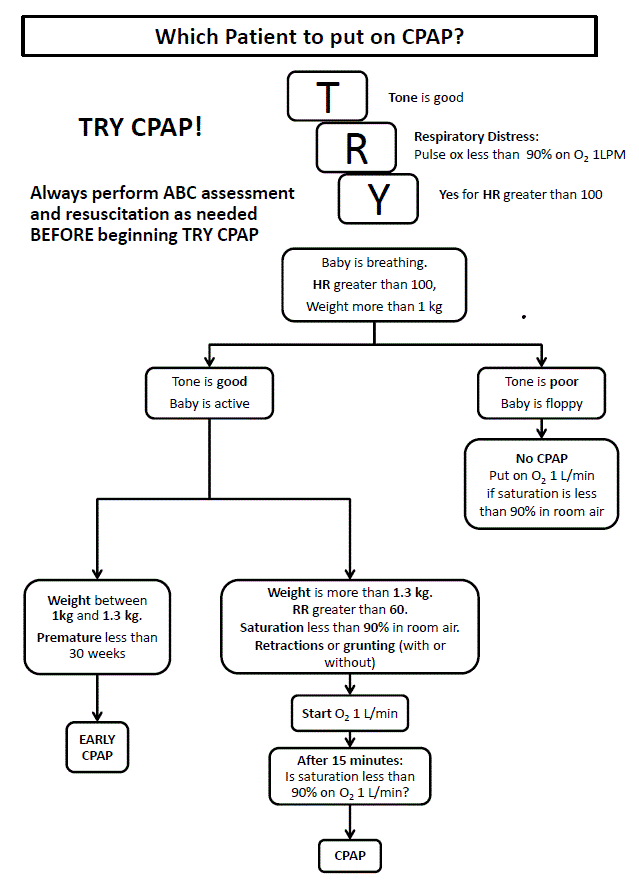
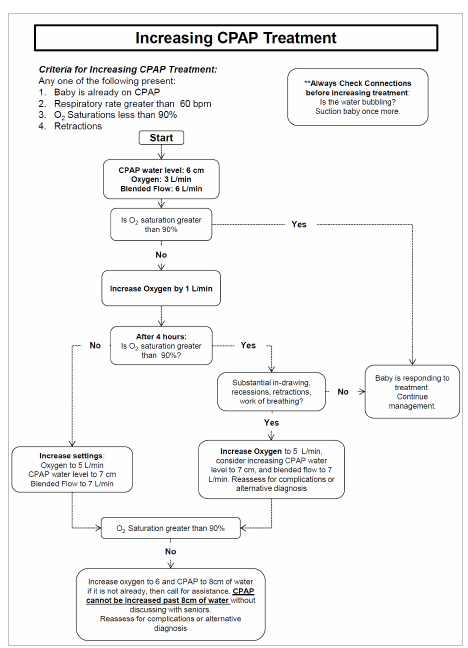
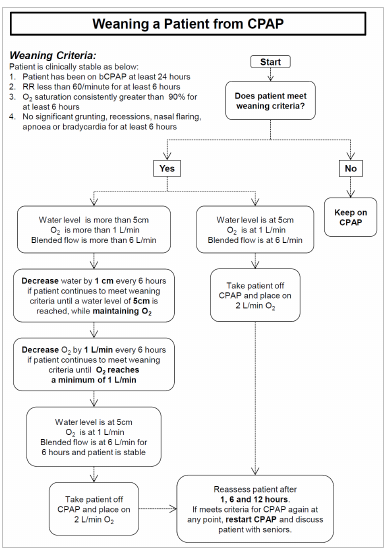 Flowcharts by Rice360 - Training Aides.
Flowcharts by Rice360 - Training Aides.