Convulsions
Causes of seizures
- Febrile convulsion with intercurrent illness e.g. malaria, viral or bacterial infection
(febrile convulsions usually occur in children 6 months - 6 years, consider other
causes in different age groups)
- Cerebral malaria
- Intracranial infections: Meningitis, Cerebral Abscess, Encephalitis
- Hypoxia of any cause
- Hypoglycaemia of any cause
- Other electrolyte or metabolic disturbances
- Cerebrovascular accidents
- Head Injury
- Seizure disorder (Epilepsy)
- Hypertensive encephalopathy
- Poisoning e.g. alcohol, tricyclic antidepressants, OPP poisoning
Differential diagnosis of seizure-like episodes
- Reflex-anoxic seizure/ Breath-holding attack leading to seizure
- 'Pseudo-seizures'
- Rigors
- Tetanus (muscle spasms)
- Rabies (agitation and spasms)
Important points in history
- Preceding symptoms of illness, fever
- Recent new neurological deficit or history of headaches
- Preceding significant head injury
- Ingestion of any medication; drug history; compliance with anticonvulsants
- PMH: seizures/ neurological illness/ disability/ developmental delay/ immunosuppression/ TB
- Family history of seizures
- Contact with source of infection e.g. meningitis case, herpes simplex
Get an exact description of the seizure and document it:
- Full description of 'fit' by an eyewitness, especially:
- What was child doing immediately before the fit?
- Did child detect a prodrome to fit? (remember it 'coming on')
- Nature of seizure: what was seen and sequence, movements of which limbs, mouth, face etc.
- WAS IT FOCAL OR GENERALISED? (may be important if epilepsy)
- Colour of the child
- Was the child responsive during the episode?
- Duration
- Incontinence/ tongue biting/ injuries sustained
- Recovery period: query post ictal
- Has full recovery been made?
- Ongoing symptoms e.g. Fever, headache, neck stiffness, rash, altered behaviour
Important points in examination
- Adequacy of: airway, breathing, circulation
- Blantyre Coma Score and behaviour (irritable, lethargic, confused?)
- Evidence of ongoing seizure activity?- Look out for subtle motor seizures
- Temperature
- Neck stiffness, Kernig's sign, rash, fontanelle
- Blood pressure
- Abnormal neurology e.g. focal signs, papilloedema, asymmetrical pupils
- Evidence of head injury
Any child with reduced conscious level or focal neurology following a seizure should
be re-examined after an interval (e.g. 1 hour) to ascertain which (if any) features are
'post-ictal', and to check for signs of deterioration.
Relevant investigations
- Blood sugar - ALWAYS if actively fitting/ reduced consciousness/ abnormal
behaviour
- Blood film for malaria parasites
- Lumbar puncture - if infection is suspected and BCS <3. No need in known epileptic patient with afebrile seizure
- Blood culture if toxic looking child or febrile infant
- U&E's if appropriate (e.g. seizures in dehydrated child)
Contraindications to lumbar puncture
- Unable to tolerate the flexed position
- Cardiovascular instability
- Features of raised ICP
|
Management
Children <2 weeks of age
Caution: DO NOT use diazepam for convulsions in neonates <2 weeks

Children >2 weeks of age
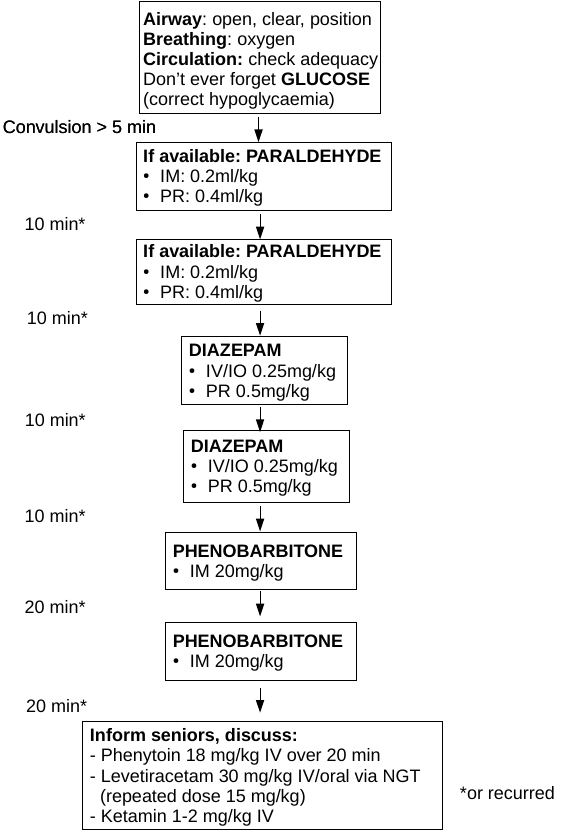
If seizures recur within 12 hours or so consider re-loading with Phenobarbitone 20mg/kg, up to three times loading within 12 hours possible. Chances to respond are low if not responded to first loading dose.
If no parenteral phenobarbitone is available consider oral given via NG tube.
Indications for admission
- Most children should be admitted when there is a history of a convulsion.
- Consider short stay ward and same day discharge for children who are known to have febrile convulsions WITH a clear focus such as URTI or uncomplicated malaria AND who are well when seen on admissions
- Known epileptics may be discharged to the care of a competent guardian if child has recovered and no concerns about ongoing management. Ensure follow-up date given in general or neurology clinic
- Consider research ward if BCS < 3
Supportive care
- Prevent recurrent hypoglycaemia if at risk (e.g. unable to take adequate feeds)
- Consider iv fluids with added dextrose, or NGT feeding if airway is safe
- Consider maintenance dose of phenobarbitone 5mg/kg/day if further seizures occur
or if a high risk of further seizures is thought to exist
- Only treat with antibiotics if
- MPs negative and clinically meningitic
- other focus of infection which needs antibiotic treatment
Guardian advice
Guardians are likely to be frightened, and need appropriate reassurance and education
- About the cause of the fits
- Risk of recurrence and any measures they can take to prevent further seizures (e.g.
avoiding prolonged fasting periods)
- Actions to take in the event of a further fit (protection from injury etc.)
- Advise NOT to insert anything into mouth of convulsing child
Is it epilepsy?
- Recurrent seizures without fever suggests epilepsy as a cause. If focal might have intracerebral process (eg tumour)
- If a seizure disorder is suspected and frequency of fits is interfering with quality of
life, the child may need to take a regular anticonvulsant, refer to a senior for decision
- Sodium valproate (for generalised epilepsy) and carbamazepine (for focal epilepsy) (when available) are better first line choice drugs than phenobarbitone
When to discharge
- Depends largely on cause of fit, and completion of cause specific treatments (for
example, infection adequately treated)
- Child must be clinically stable, fully conscious, behaving normally (unless a chronic
neurological disability remains), and not at high immediate risk of further fits as far as
can be predicted.
Follow up
- If epilepsy, give date for general clinic (1.30 pm Wednesday)
- Consider neurology clinic (Thursday morning) if 'complicated' epilepsy - discuss with Dr. Mallewa
- If ongoing disability, consider what supports might be available to the child and family e.g. QECH rehab. (discuss with Mrs Dorothy Chinguo, Feed The Children) for physiotherapy, mobility aids, Umodzi
| Guardians should be adequately informed about risk of further fits and
what to do if they occur |
