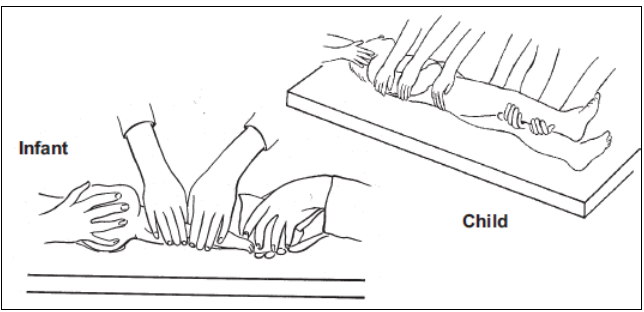
| >5 years |
<5 years |
| Motor |
|
| Obeys commands (6) |
Normal spontaneous movements (6) |
| Localises pain (5) |
Withdraws to touch (5) |
| Withdraws to pain (4) |
Withdraws to pain (4) |
| Flexion to pain (decorticate) (3) |
Abnormal flexion (decorticate) (3) |
| Extension to pain (decerebrate) (2) |
Abnormal extension (decerebrate) (2) |
| No response (1) |
No response (1) |
| Verbal |
|
| Orientated (in person or place or address)
(5) |
Alert, babbles, words or sentences to usual ability (normal) (5) |
| Confused (4) |
Less than usual ability, irritable cry (4) |
| Inappropriate words (3) |
Cries to pain (3) |
| Incomprehensible sounds (2) |
Moans to pain (2) |
| No response to pain (1) |
No response to pain (1) |
| Eyes |
|
| Spontaneous (4) |
Spontaneous (4) |
| To voice (3) |
To voice (3) |
| To pain (2) |
To pain (2) |
| None (1) |
None (1) |