Meningitis in NYI (Chapter 17)
Learning Objectives
After completion of this chapter the participant should be able to:
- Define meningitis.
- Describe how a NYI with meningitis may present.
- Describe the management management of a NYI with meningitis,
See supportive care care of meningitis
See investigations in case of suspicion
of meningitis
Definition of Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges.
Symptoms and Signs
Suspect meningitis in an infant with
sepsis or if they present with the following clinical
symptoms or signs:
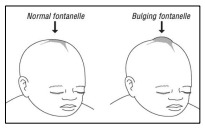
Note: NYI often do not have neck stiffness
Investigations
To confirm the diagnosis of meningitis, a lumbar puncture must be done immediately unless the
young infant is convulsing actively or is unstable.
Also a blood culture, urine dipstick, microscopy and culture if available or a urine analysis.
Empiric therapy for meningitis: How to calculate the dose
For doses see
wall charts
| ANTIBIOTIC |
EACH DOSE |
FREQUENCY |
ROUTE |
| Age <7 days |
Age >7 days |
Benzyl
penicillin |
100,000 IU/kg |
12 hrly. |
6 hrly. |
IV |
| AND |
| Gentamicin |
LBW 3 mg/kg/dose
Term 5 mg/kg/dose for 1st week
>7 days 7,5 mg/kg/dose |
24 hrly. |
24 hrly. |
IV |
| OR |
| Ceftriaxone |
100 mg/kg/dose |
24 hrly. |
24 hrly. |
IV |
Key Facts for Providers:
Supportive Care for NYI with Meningitis |
- Ensure warmth.
- Respiratory support with oxygen or CPAP if there is severe respiratory distress
or apnoea.
- Gentle stimulation if apnoeic, consider aminophylline if premature and current
age is estimated to be <37 weeks gestation.
- If shocked treat according to the impaired circulation protocol.
- If hypoglycaemic, infuse 2mls/kg of 10% dextrose stat and recheck in 30 minutes,
continue maintenance 10% dextrose.
- Treat convulsions if present
- Treat jaundice if present with phototherapy
- If very sick, e.g., continuous convulsions, avoid oral feeds, give
maintenance fluids.
- If they have not received Vitamin K, give 1mg to term baby or 0.5 mg to premature
babies intramuscularly.
- Reassess therapy based on culture and antibiotic sensitivity results if possible.
- Continue IV antibiotics for at least 2 weeks (e.g., for GBS) or 3 weeks (for Gram
negative bacteria).
- If the organism is not known, but it is known that the baby has meningitis, then the
safest duration to give antibiotics is for 3 weeks to cover for the possibility of Gram
negative bacteria causing the meningitis.
- Measure the NYI head circumference every 3 days as an intracranial abscess or
hydrocephalus may develop. If circumference is increasing, do a cranial ultrasound
scan.
|
